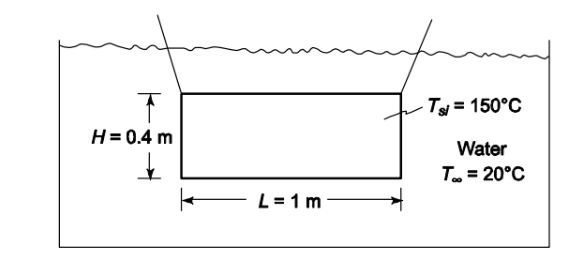
An aluminum sheet, 0.4-m-tall, 1-m-long, and 0.002-m-thick is to be cooled from an initial temperature of 150°C to 50°C by immersing it suddenly in water at 20°C. The sheet is suspended from two wires at the upper corners as shown in the sketch.
(a) Determine the initial and the final rate of heat transfer from the plate.
(b) Estimate the time required.
(Hint: Note that in laminar natural convection, h ? ?T 0.25)
GIVEN
• A vertical aluminum sheet in water
• Plate dimensions: height (H) = 0.4 m, length (L) = 1 m, thickness (s) = 0.002 m
• Initial plate temperature (Tsi) = 150°C
• Water temperature (T?) = 20°C
• Final plate temperature (Tsf) = 50°C
FIND
(a) The initial and final heat transfer rates
(b) The time required
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant and uniform water temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for aluminum at the mean temperature of 100°C
Thermal conductivity (ka1) = 238 W/(m K)
Density (?) = 2702 kg/m3
Specific heat (c) = 896 J/(kg J)
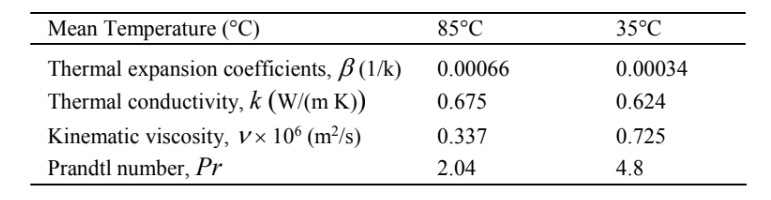
(a) The Grashof number based on the height of the plate is
Initial
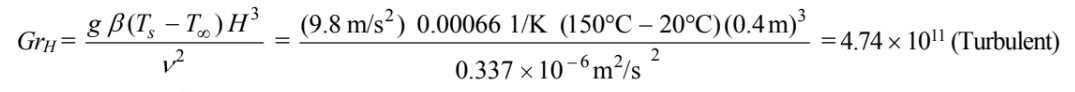
Final
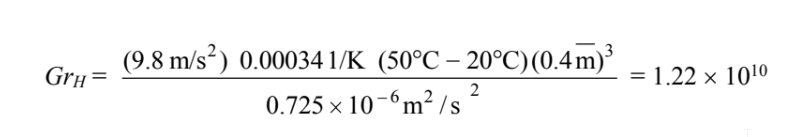
(Turbulent)
The average heat transfer coefficient from a vertical plate with a turbulent boundary layer is
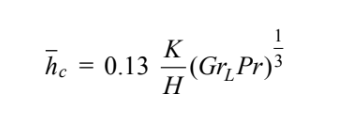
Initial
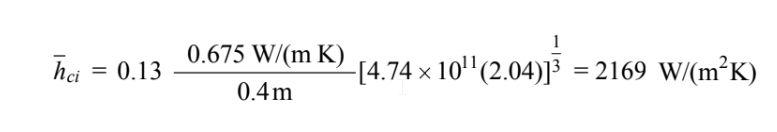
Final
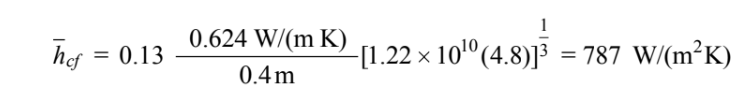
The rate of convective heat transfer from the plate is
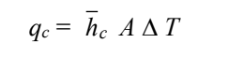
Initial
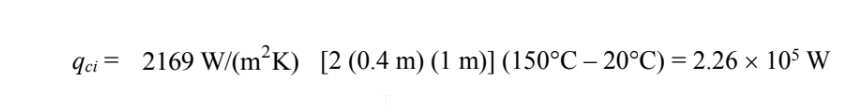
Final
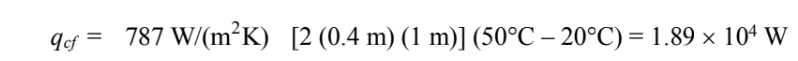
(b) The initial Biot number for the aluminum sheet is
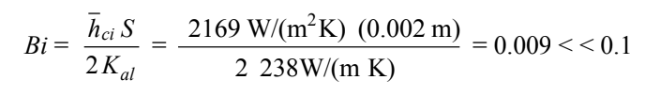
Therefore, the internal thermal resistance of the aluminum sheet is negligible during the entire cool down and the temperature-time history of the sheet is
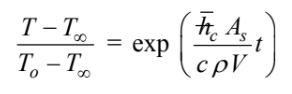
Solving for the time
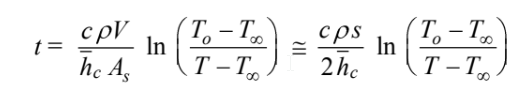
Using the average of the initial and final heat transfer coefficients
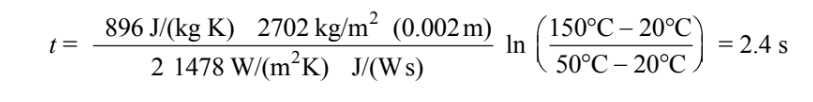
You might also like to view...
Relative Velocity: Alicia intends to swim to a point straight across a 100 m wide river with a current that flows at 1.2 m/s. She can swim 2.5 m/s in still water. At what angle, measured from the upstream direction, must she swim upstream to achieve her goal?
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Light passes from a material with index of refraction 1.1 into one with index of refraction 1.5 after being incident at a non-normal angle (?inc ? 0). Compared to the incident ray, the refracted ray will
1.be unaffected. 2.bend towards the normal. 3.follow the normal. 4.bend away from the normal.
Stable equilibrium is:
a. an equilibrium state where any small rotation results in a torque that acts to produce rotation back in the opposite direction. b. any form of equilibrium, because all equilibrium conditions are stable. c. an equilibrium state where nothing is moving. d. an equilibrium state where there is no net torque or net force. e. an equilibrium state where no torque is involved.
Buoyancy: A hollow steel ball of diameter 3.0 m just barely floats in water. What is the wall thickness of the ball? (?Fe = 7.87 g/cm3, ?water = 1.00 g/cm3)
A. 6.6 cm B. 37 cm C. 131 cm D. 79 cm