The marginal product of labor can be defined as:
a. the change in profit divided by the change in labor, other factors of production held constant
b. the change in total output provided by a one unit increase in labor employed, other factors of production held constant.
c. the total output divided by the total labor utilized.
d. the change in labor utilized divided by the change in total output, other factors of production held constant.
b
You might also like to view...
Which of the following must be true if a price-searcher firm is operating at the profit-maximizing output rate?
a. The marginal cost of producing the last unit is greater than the marginal revenue derived from its sale. b. The marginal cost of producing the last unit is no greater than the marginal revenue derived from its sale. c. The total cost of producing all units is no greater than the total revenue derived from the sale of the units. d. The total cost of producing all units is less than the total revenue derived from the sale of the units.
In which of the following models of firm behavior do firms make strategic pricing decisions and also charge a perfectly competitive price?
A. Contestable market model of oligopoly B. Monopoly model C. Perfectly competitive model D. Cartel model of oligopoly
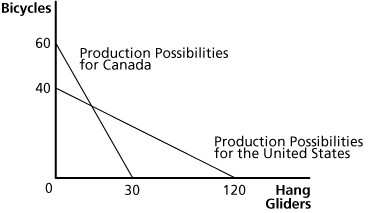 Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. The opportunity cost of hang gliders in Canada is:
Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. The opportunity cost of hang gliders in Canada is:
A. 1/4 of a bicycle. B. 1/2 of a bicycle. C. 2 bicycles. D. 4 bicycles.
Suppose the demand function for a good is expressed as Q = 100 - 4p. If the good currently sells for $10, then the price elasticity of demand equals
A) -1.5. B) -0.67. C) -4. D) -2.5.