Holding all variables constant but one and assessing the impact of the one variable that has changed is an example of using
A. the ceteris paribus assumption.
B. an untestable proposition.
C. an economic model based on unrealistic assumptions.
D. a flawed economic model.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Owners of ________ have unlimited liability
A) partnerships and corporations B) corporations C) proprietorships and partnerships D) partnerships, proprietorships, and corporations
Which of the following is not a property of isoprofit curves graphed in Probability of Injury (x-axis) versus Wage (y-axis) space?
A. Profit-maximizing firms are indifferent as to where they operate on any given curve. B. All points on each isoprofit curve yield the same level of profit. C. Isoprofit curves going up along the y-axis yield higher profits. D. Isoprofit curves going out along the x-axis yield higher profits. E. Isoprofit lines are upward sloping.
New residential housing is counted in GDP as a(n):
A. durable consumption good. B. household durable good. C. investment good. D. inventory expansion.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 3.14 below to answer the question(s) that follow.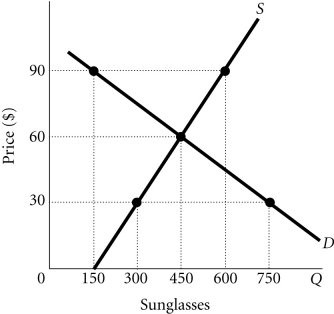 Figure 3.14Refer to Figure 3.14. If this market is unregulated and the price is currently $30, you would expect that the price of sunglasses would
Figure 3.14Refer to Figure 3.14. If this market is unregulated and the price is currently $30, you would expect that the price of sunglasses would
A. rise to $60, where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. B. rise to $90, so the firm could meet its excess demand. C. remain at $30, because firms would not want to increase the price. D. rise, but the new price is indeterminate from the information provided.