In a perfectly competitive long-run constant-cost industry, an increase in market demand causes:
A. an increase in quantity, no change in price, and no change in profit in the long run.
B. an increase in price, quantity, and profit in the long run.
C. an increase in quantity, a decrease in price, and no change in profit in the long run.
D. a decrease in price, a decrease in quantity, and a decrease in profit in the long run.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question.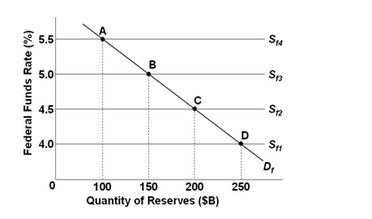 If the federal funds market is at equilibrium at point C and the Federal Reserve decides to conduct an open-market sale, then it must be trying to set a ________.
If the federal funds market is at equilibrium at point C and the Federal Reserve decides to conduct an open-market sale, then it must be trying to set a ________.
A. lower target federal funds rate by increasing the amount of reserves in the market B. higher target federal funds rate by increasing the amount of reserves in the market C. higher target federal funds rate by reducing the amount of reserves in the market D. lower target federal funds rate by reducing the amount of reserves in the market
In January 2015, Tim's Gyms, Inc owned machines valued at $1 million. During the year, the market value of the equipment fell by 30 percent. During 2015, Tim spent $200,000 on new machines. During 2015, Tim's gross investment totaled
A) $1 million. B) $300,000. C) $200,000 D) $900,000.
The regulatory lag:
A) always benefits the regulated firm. B) is likely to occur with rate-of-return regulation. C) promotes economic efficiency. D) all of the above
A decrease in long-run average costs resulting from decreases in output is
A. attributed to diseconomies to scale. B. attributed to economies of scale. C. attributed to constant returns to scale. D. attributed to the law of diminishing marginal product.