The principle of comparative advantage essentially states that
A) there are some goods for which the opportunity costs of production are the same regardless of who produces them.
B) some goods have high opportunity costs and low absolute costs.
C) specialization can reduce output rather than increase it.
D) total output of an economic system is greatest when each good is produced by those who have the lowest opportunity cost of producing the good.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is false?
a. People looking for full-time work who grudgingly settle for a part-time job are counted as employed, even though they are only "partly" employed. b. Some people working in the underground economy could be counted in labor statistics as unemployed, while others may be counted as not in the labor force. c. Unemployment rates can be quite different across different segments of the population, as well as varying substantially over time. d. None of the above are false; all are true.
When exports exceed imports there is a(n):
A. trade balance. B. trade surplus. C. output gap. D. trade deficit.
Exhibit 6-1 Business cycle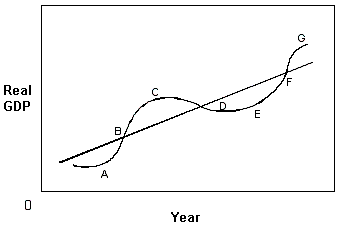
A. A. B. C. C. E to G. D. C to E.
The supply curve will be more inelastic when:
A. inputs to production are scarce. B. firms' response to a price change is limited by the limited capacity of their production facilities. C. a good has many substitutes. D. the firm is experiencing diminishing returns to a variable input.