A tungsten wire is 1.50 m long and has a diameter of 1.00 mm. At 20°C a current of 50 mA flows through this wire
The temperature coefficient of resistivity for this tungsten is 4.5 × 10-3/C°, and its resistivity at 20°C is 5.6 × 10-8 ? ? m.
(a) What is the potential difference across the ends of this wire at 20°C?
(b) If the wire temperature increases by 100 C°, what potential difference across its ends is now required to produce a current of 50 mA?
(a) 5.3 mV (b) 7.8 mV
You might also like to view...
If the accuracy in measuring the position of a particle increases, the accuracy in measuring its velocity will
A) increase. B) decrease. C) remain the same. D) It is impossible to say since the two measurements are independent and do not affect each other.
A point charge +Q is located on the x axis at x = a, and a second point charge -Q is located on the x axis at x = -
a. A Gaussian surface with radius r = 2a is centered at the origin. The flux through this Gaussian surface is a. zero because the negative flux over one hemisphere is equal to the positive flux over the other. b. greater than zero. c. zero because at every point on the surface the electric field has no component perpendicular to the surface. d. zero because the electric field is zero at every point on the surface. e. none of the above.
Specific Heat: Object 1 has three times the specific heat capacity and four times the mass of Object 2. The two objects are given the same amount of heat. If the temperature of Object 1 changes by an amount ?T, the change in temperature of Object 2 will be
A. ?T.
B.  ?T.
?T.
C. 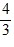 ?T.
?T.
D. 6?T.
E. 12?T.
An FM radio tuning circuit has a coil with an inductance of 0.0036 mH. What is the value of the capacitance if the set is tuned to 91.3 MHz?
a. 3.38E–12 F b. 2.65E–12 F c. 4.84E–13 F d. 8.45E–13 F e. 8.33E–12 F