Higher nominal interest rates ________ the amount of money demanded and higher real income ________ the amount of money demanded.
A. increase; increases
B. increase; decreases
C. decrease; decreases
D. decrease; increases
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob is
A) risk averse. B) risk neutral. C) risk loving. D) risk premium.
As inflation drives up prices, people attempt to find substitutes and adjust what they buy. The resulting substitution bias problem causes the CPI to
a. overstate the impact of higher prices on consumers. b. consistently underestimate the true inflation rate. c. omit the benefits of product quality improvements. d. have larger fluctuations than other price indexes.
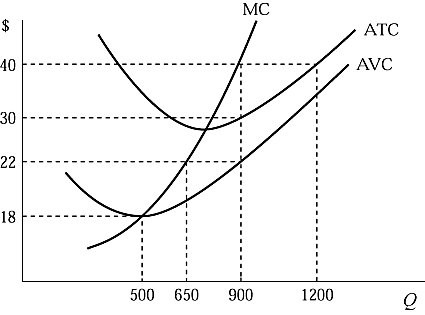
 Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing output level, its total fixed cost is:
Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing output level, its total fixed cost is:
A. $2,800. B. $5,200. C. $7,200. D. $9,000.
The long run is defined as a time period during which full adjustment can be made to any change in the economic environment. Thus in the long run, all factors of production are variable. Long-run curves are sometimes called planning curves, and the long run is sometimes called the
A. non-adjustment period. B. planning horizon. C. foreseeable future. D. minimum efficient time period.