The envelope of enveloped viruses
A. does not contain spikes.
B. is identical to the host plasma membrane.
C. is only composed of host endomembrane.
D. makes the virus very susceptible to drug therapy.
E. is obtained by viral budding or exocytosis.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Based on the following graph, what is the most likely relationship between Paramecium and Didinium?
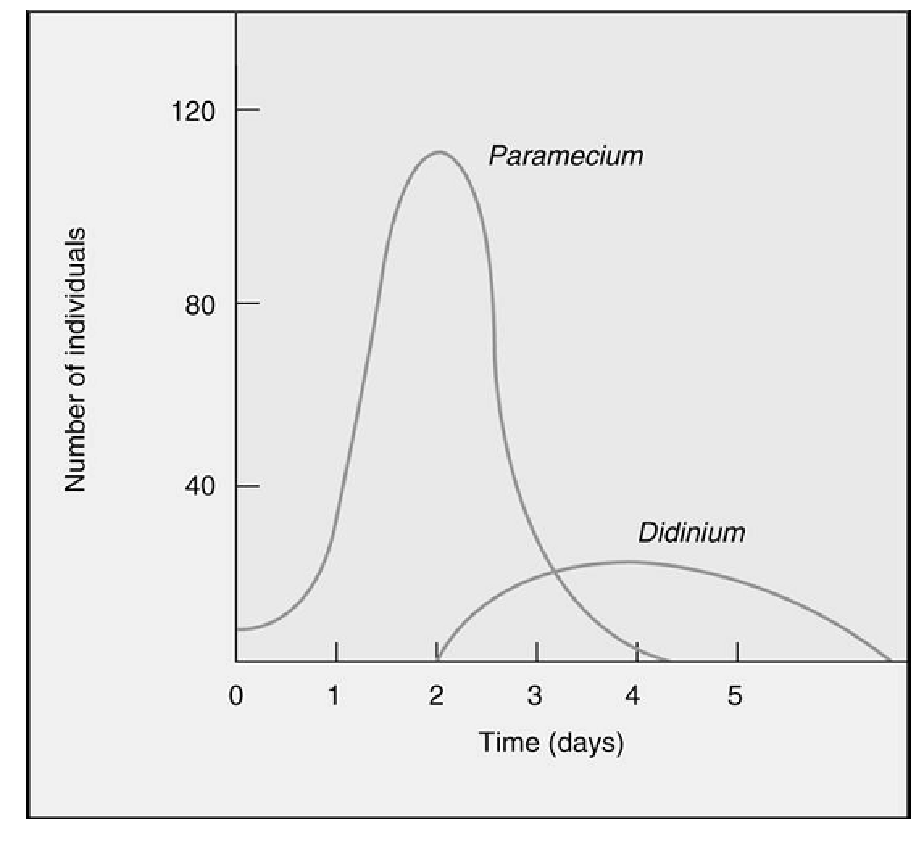
A. Paramecium prey on Didinium.
B. Paramecium have a commensal relationship with Didinium.
C. Didinium and Paramecium have a mutualistic relationship.
D. Didinium prey on Paramecium.
E. Paramecium is a parasite that feeds on Didinium.
Clarify question:
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content:
What do you already know about relationship between the two species? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer:
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflection:
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Which of the following equations is correct?
A) resistance = (length × radius4) / viscosity B) cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate C) mean arterial pressure = resistance × viscosity D) mean arterial pressure = cardiac output × stroke volume E) cardiac output = mean arterial pressure × total peripheral resistance
Which method is often used to analyze proteins and nucleic acids by physical separation when estimating genetic variation in populations?
A) centrifugation B) fluorometry C) in situ hybridization D) electrophoresis E) absorption spectrophotometry
Which of the following is the correct explanation for the data?
(A) At higher osmolarity, lower rates of contraction are required because more salt diffuses into the paramecia. (B) The contraction rate increases as the osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering the paramecia by osmosis increases. (C) The contractile vacuole is less efficient in solutions of high osmolarity because of the reduced amount of ATP produced from cellular respiration. (D) In an isosmotic salt solution, there is no diffusion of water into or out of the paramecia, so the contraction rate is zero.