An astronaut tosses a ball out in space where gravitational forces may be neglected. What will happen to the ball?
a. It will stop as soon as the force the astronaut gave it is used up.
b. It will stop when the energy the astronaut gave it runs out.
c. It will stop after a short time because there is no gravity to keep it moving.
d. It will move in a circle like a boomerang.
e. It will be slowed down very gradually by collisions with molecules in space.
e
You might also like to view...
Phase Angles: The phase angle of a series RL ac circuit with a 100-? resistor and a 20.0-mH inductor is 70.0°. What is the inductive reactance of this circuit?
A. 100 ? B. 150 ? C. 200 ? D. 175 ? E. 275 ?
A 2.0-C charge moves with a velocity of (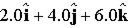
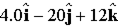
A. ?3.0 T B. +3.0 T C. +5.0 T D. ?5.0 T E. +6.0 T
Which answer below is not a statement of the second law of thermodynamics?
a. Real processes proceed in a preferred direction. b. Energy does not flow spontaneously by heat from a cold to a hot reservoir. c. The entropy of the universe increases in all natural processes. d. In theory, heat engines working in a cycle employ reversible processes. e. You cannot construct a heat engine, operating in a cycle that does nothing but take heat from a reservoir and perform an equal amount of work.
Which of the following statements is(are) correct when an ideal gas goes from an initial to a final state in a single process?
a. No work is done on or by the gas when the volume remains constant. b. No energy is transferred into or out of the gas as heat transfer when the temperature remains constant. c. The internal energy of the gas does not change when the pressure remains constant. d. All the statements above are correct. e. Only statements (a) and (b) above are correct.