According to the Romer model, tax incentives to support research and development will lead to ________
A) higher tax rates in the future
B) an increase in the general level of prices
C) a decrease in the general level of prices
D) increased per capita income
D
You might also like to view...
The theory of optimum currency areas predicts that
A) floating exchange rates are most appropriate for areas closely integrated through international trade and factor movements. B) fixed exchange rates are most appropriate for areas that are loosely integrated through international trade and factor movements. C) fixed exchange rates are most appropriate for areas closely integrated through international trade and factor movements. D) floating exchange rates are most appropriate for all countries in Europe. E) fixed exchange rates are most appropriate for all countries in Europe.
Several countries in the world have failed to “converge” with industrialized countries. What does this mean about their economic growth rates? Explain why poorer countries have failed to "catch up," in terms of the pillars of economic growth. Are there any special problems facing these countries?
What will be an ideal response?
Assume that the substitution effect dominates the income effect. An increase in both consumption and labor supply would result from
A. a decrease in tax rates. B. an increase in tax rates. C. an increase in transfer payments. D. a decrease in transfer payments.
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $10, and lump-sum taxes also increased from $0 to $10, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
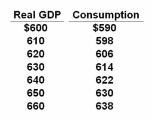
The table shows the consumption schedule for a hypothetical economy. All figures are in billions of dollars.
A. $660
B. $630
C. $640
D. $650