The demand curve in its home market is P = 200 - Q; the demand curve in its foreign market is P = 160 - 2Q; and its marginal cost is a constant $20 per unit. What is the discriminating monopolist's profit maximizing output in the foreign market?
a. 90
b. 110
c. 70
d. 35
Ans: d. 35
You might also like to view...
Suppose you borrow $8,000 for one year and at the end of the year you repay the $8,000 plus $600 of interest. The expected inflation rate was 3.5% at the time you took out the loan, but the actual inflation rate turned out to be 2.5%
What was the expected real interest rate at the time of the loan? What was the actual real interest rate you paid? Who gained and who lost from the difference in the expected and actual inflation rates?
Figure 4-13
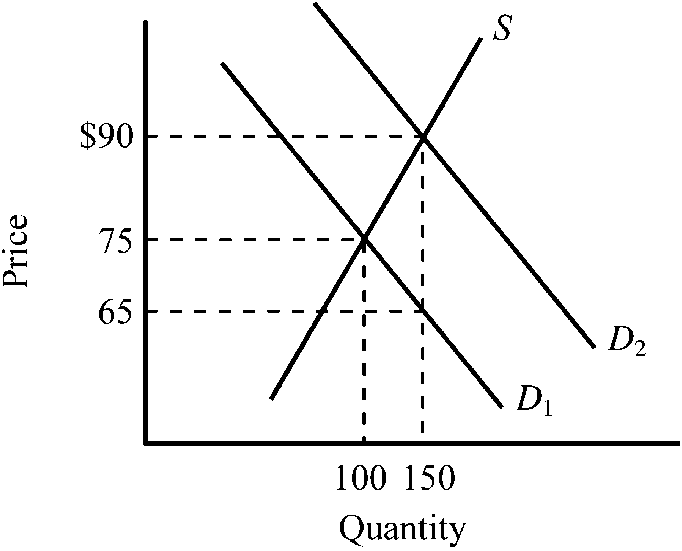
Refer to . The exhibit illustrates the impact of granting a subsidy on a particular good. Which of the following is true for this subsidy given the information provided in the exhibit?
a.
The subsidy has been statutorily (legally) paid to sellers.
b.
The subsidy results in a decrease in the market selling price of the good.
c.
Sellers will receive a larger proportion of the benefit from this subsidy than buyers.
d.
The subsidy results in a reduction in the quantity purchased.
Peak load pricing helps firms gain profit because
A. people are willing to pay more for the first units they consume of a good. B. low prices when demand is strong means high volume sales. C. they can serve their customers with a smaller capital base. D. demand shifts left during peak load hours.
During the recession in 2001, President Bush extended the effectiveness of the automatic stabilizers by
A. giving tax credits to companies. B. increasing transfer payments to needy. C. permitting unemployed to receive for an additional 13 week period. D. increasing the excise expensive automobiles.