Entrepreneurship
A. Can result in economic losses.
B. Always involves greater rewards than risks.
C. Occurs in small businesses, but not large corporations.
D. Cannot earn an economic profit.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A constant-cost, perfectly competitive market is in long-run equilibrium. At present, there are 1,000 firms each producing 400 units of output. The price of the good is $60
Now suppose there is a sudden increase in demand for the industry's product which causes the price of the good to rise to $64. In the new long-run equilibrium, how will the average total cost of producing the good compare to what it was before the price of the good rose? A) The average total cost will be the same as it was before the price increase. B) The average total cost will be lower than it was before the price increase because of economies of scale. C) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase because of diseconomies of scale arising from the increased demand. D) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase since the increase in demand will drive up input prices.
A private good is:
a. excludable and nonrival. b. nonexcludable and rival. c. nonexcludable and nonrival. d. excludable and rival.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 23.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.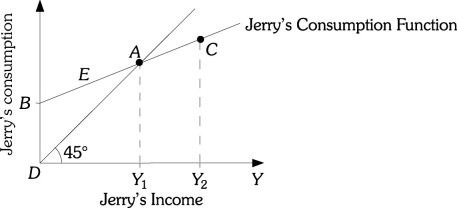 Figure 23.2Refer to Figure 23.2. An increase in Jerry's income is represented by
Figure 23.2Refer to Figure 23.2. An increase in Jerry's income is represented by
A. a movement from Point B to A. B. an increase in the slope of Jerry's consumption function. C. an upward shift in Jerry's consumption function. D. none of the above.
Describe the three major units of the Federal Reserve System and their functions.
What will be an ideal response?