Refer to the table below. If the senior manager learns that either a Fair or Poor market will exist when the drug is introduced to the market, which drug should the senior manager pursue?
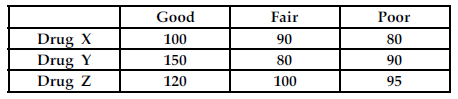
The senior manager of Rx Pharmaceuticals needs to decide which of three drugs the company should consider developing. The estimated profit for each of the drugs differs depending on the market conditions when the respective drugs are introduced to the market. The above table summarizes the estimated profit for each drug under each of the three market conditions; Good, Fair, and Poor.
A) Drug Z
B) Drug X
C) Drug Y
D) none of the drugs
A) Drug Z
You might also like to view...
The above figure represents the market for professional minor-league baseball umpires
a) If umpires are offered $90 a game, what is the quantity of umpires supplied? b) If umpires are offered $90 a game, is there a surplus or shortage of games umpired? What does the shortage or surplus equal? c) What is the equilibrium wage rate and quantity of umpires?
Andre Agassi, a star tennis player, is playing the number one player in the world, Roger Federer
Before the match, Agassi decided that he would serve 20 percent of his serves to Federer's backhand, 30 percent of his serves to Federer's forehand, and 50 percent of his serves straight at Federer. In the language of game theory, this is known as: A) a pure strategy. B) a dominant strategy. C) a mixed strategy. D) a maximin strategy.
A model can be accurately described as a
a. theoretical abstraction with very little value. b. device that is useful only to the people who created it. c. realistic and carefully constructed theory. d. simplification of reality.
If you observe that Kelly Clarkson won American Idol 3 years before Carrie Underwood won, and you conclude that Kelly Clarkson winning caused Carrie Underwood to win 3 years later, you would be guilty of an error called the
A. fallacy of ceteris paribus. B. post hoc, ergo propter hoc fallacy. C. fallacy of logic. D. fallacy of inductive reasoning.