If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and observes a market price of $13, the firm:
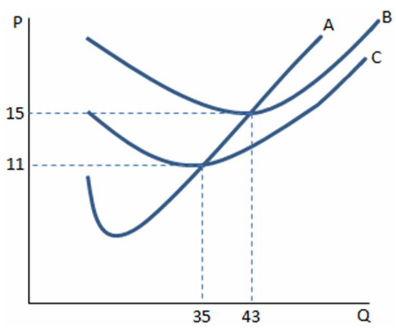
A. can make positive profits by producing more than 35 units.
B. can make positive profits by producing where MC = MR.
C. cannot make positive profits and should shut down in the short run.
D. should continue to operate in the short run, but plan to exit in the long run.
D. should continue to operate in the short run, but plan to exit in the long run.
You might also like to view...
In the figure above, the poorest 20 percent of households receive ________ of total income
A) 20 percent B) 10 percent C) 5 percent D) 15 percent
An exception to the law of one price occurs if
A) the good is not tradeable. B) demand for the good is stronger in some countries than in others. C) exchange rates are flexible, rather than fixed. D) interest rates differ across countries.
The third round of quantitative easing, announced in September 2012, was focused on purchases of:
A) short-term Treasury bills B) long-term Treasury notes C) long-term Treasury notes and sales of short-term Treasury bills D) mortgage-backed securities
Prior to the 1880s, federal government control over the daily operations of private economic activity
(a) was important but not as important as during the 1880s and following decades. (b) was virtually nonexistent; state and local governments handled any regulation or business management. (c) was important, but in the 1880s and following decades, it became less important as it was realized that regulation was basically inconsistent with the efficient operation of free markets. (d) was virtually nonexistent and did not become important until the Great Depression and New Deal programs of the 1930s.