Suppose we are at a long-run equilibrium point in an AD-AS model. Then the money supply increases. In the short run, is there any difference between what happens in the simple quantity theory of money (SQTM) version and the monetarist version of the model?
A) There is no difference.
B) In the SQTM version, the price level rises; in the monetarist version, it does not.
C) In the monetarist version, the price level falls; in the SQTM version, it does not.
D) In the monetarist version, the Real GDP rises; in the SQTM version, it does not.
E) In the SQTM version, Real GDP falls; in the monetarist version, it does not.
D
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. The major reason education leads to higher wages is due to signaling. 2. Attending college can be seen as an individual’s attempt to raise their level of human capital. 3. Since mowing ones lawn is not done at their workplace, it is viewed as a use of their leisure time and thus (somewhat paradoxically) falls into the category of leisure. 4. One deficiency of labor-leisure indifference curve analysis is that because indifference curves are always tangent to the worker’s budget line, the model can not explain why some people choose not to work. 5. A firm’s marginal revenue product of labor equals the marginal product of labor times the cost per unit of the labor.
Assume MUc and MUd represent the marginal utilities that Alyssa receives from the consumption of products C and D, respectively. Given a fixed budget, Alyssa could increase her total utility by spending more on C and less on D if initially
A. 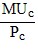 >
> 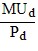
B. MUd > MUc
C. MUd < MUc
D. 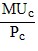 <
< 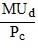
The figure above shows the market for umbrellas in Sunville. When the market for umbrellas in Sunville is in equilibrium, what is the consumer surplus?
A) $30 B) $9,000 C) $18,000 D) $16,000
A firm encounters its "shutdown point" when:
A) average total cost equals price at the profit-maximizing level of output. B) average variable cost equals price at the profit-maximizing level of output. C) average fixed cost equals price at the profit-maximizing level of output. D) marginal cost equals price at the profit-maximizing level of output.