Refer to the information provided in Figure 12.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.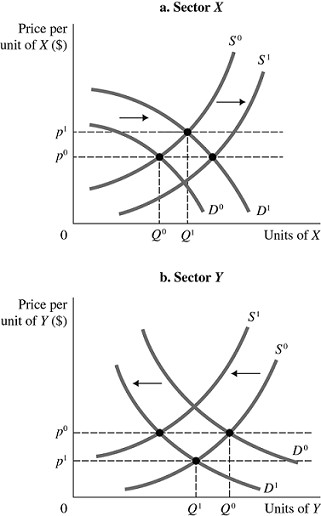 Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flows in sectors X and Y will eventually________ in industry X and ________ in industry Y.
Figure 12.4There are two sectors in the economy, X and Y, and both are in long-run, zero-profit equilibrium at the intersections of S0 and D0.Refer to Figure 12.4. Assume consumer preference changes toward X and away from Y. Ceteris paribus, the likely change in capital flows in sectors X and Y will eventually________ in industry X and ________ in industry Y.
A. decrease the price to P0; decrease the price to P1
B. increase the price to P1; decrease the price to P1
C. increase the price to P1; increase the price to P0
D. decrease the price to P0; increase the price to P0
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
A an example of a game in which a leader moves first, and then the other rivals follow is a ________ game
A) Stackelberg model B) Cournot model C) finite move D) tit-for-tat
A bank may hold secondary reserves, such as U.S. government securities because:
a. they pay higher interest rates than deposits at the Fed, and are easily converted into cash assets. b. they pay higher interest rates than deposits at the Fed, even though they are hard to convert assets. c. they pay lower interest rates than deposits at the Fed, but are more easily converted into cash assets. d. they pay lower interest rates than deposits at the Fed, and are hard to convert into cash assets.
The economy's normal, long-run growth rate is shown in the AD-AS model as:
A. the upward-sloping SRAS curve. B. the vertical LRAS curve. C. the vertical SRAS curve. D. the horizontal LRAS curve.
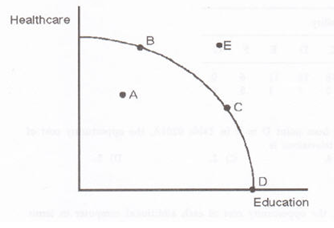
15) In the figure above, the opportunity cost of moving from point B to point C A) is the loss in production in the healthcare sector. B) is the increase in production in the education sector. C) is zero. D) is the loss in production in the education sector.