Using Figure 4.2, match the following:
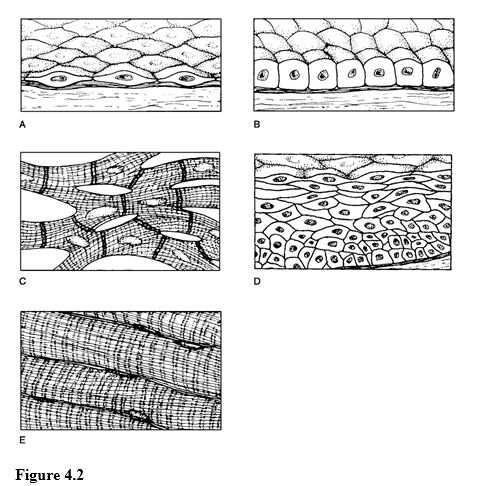
1) Simple cuboidal epithelium.
2) Cardiac muscle.
3) Simple squamous epithelium.
4) Stratified squamous epithelium.
5) Skeletal muscle.
1) B
2) C
3) A
4) D
5) E
You might also like to view...
Conductive activity in a neuron generally causes it to secrete
A. a specific neurotransmitter that either excites or inhibits its target. B. a specific neurotransmitter that always excites its target. C. several types of neurotransmitters simultaneously, all of which excite the cell's target. D. several types of neurotransmitters simultaneously, that are broadcast to excite and inhibit multiple targets. E. several types of neurotransmitters simultaneously, that all work to prevent another immediate impulse.
Adrenoleukodystrophy is caused by deficiency of a protein in the outer membrane of
A) cells. B) peroxisomes. C) lysosomes. D) mitochondria.
Which muscle inserts on the thyroid cartilage of the larynx?
A) geniohyoid B) digastrics C) sternothyroid D) sternohyoid
Which of the following statements accurately describes the solutes within a solution?
A. Solutes are greater than 1 millimeter in size, and will settle out of solution if the mixture is left standing. B. Solutes are between 1 nanometer and 1 millimeter in size; they do not scatter light but will settle out of solution if left standing. C. The solutes are not visible, do not scatter light, and do not settle if the solution is left standing. D. Water is the universal solute, and solutes are more abundant in solutions than solvents are.