A 46.0-kg crate, starting from rest, is pulled across a floor with a constant horizontal force of 225 N. For the first 11.0 m the floor is frictionless, and for the next 10.0 m the coefficient of friction is 0.20. What is the final speed of the crate after being pulled these 21.0 m?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer:
net work done on the crate = F*(d1+d2) - mue*m*g*d2
= 225*(11+10) - 0.2*46*9.8*10
= 3823.4 J
work done = chnage in kinetic enrgy
3823.4 = 0.5*m*v^2
v = sqrt(2*3823.4/46)
= 12.893 m/s
You might also like to view...
Thermal Expansion: A large vat contains 1.000 L of water at 20°C. What volume will this water occupy when it is heated up to 80°C? Water has a volume expansion coefficient of 210 × 10-6 K-1.
A. 1.600 L B. 1.013 L C. 0.987 L D. 0.9987 L
Capacitors in Combination: A system of four capacitors is connected across a 90-V voltage source as shown in the figure.(a) What is the potential difference across the plates of the 6.0-µF capacitor?(b) What is the charge on the 3.0-µF capacitor?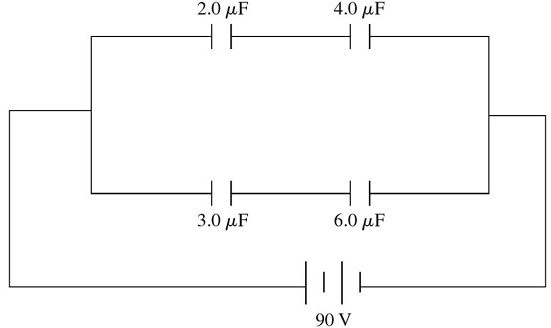
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The kilogram is currently defined as
A) the mass of a platinum-iridium cylinder kept in Sévres, France. B) the weight of a platinum-iridium cylinder as measured on the Earth's moon. C) the mass of 5.9786332 × 1026 protons. D) the mass of one liter of pure water, free of air, at standard temperature and pressure. E) the mass of a cube of pure water, free of air, 10 cm on each side, at standard temperature and pressure.
The formula mass for C2H6 is ______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word