Refer to the table below. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 50 percent chance of being $6 and a 50 percent chance of being $8. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
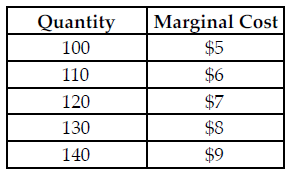
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 110
B) 140
C) 130
D) 120
D) 120
You might also like to view...
John is trying to decide how to divide his time between his job as a stocker in the local grocery store, which pays $7 per hour for as many hours as he chooses to work, and cleaning windows for the businesses downtown. He makes $2 for every window he cleans. John is indifferent between the two tasks, and the number of windows he can clean depends on how many hours he spends cleaning in a day, as shown in the table below:Hours PerDay CleaningWindowsTotal Numberof WindowsCleaned0017211314416517How many hours a day should John spend cleaning windows?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
Suppose that the prices of good A and good B were to suddenly double. If good A is plotted along the horizontal axis,
A) the budget line will become steeper. B) the budget line will become flatter. C) the slope of the budget line will not change. D) the slope of the budget line will change, but in an indeterminate way.
In the long run, a year-long drought that destroys most of the summer's wheat crops causes permanently:
A. higher prices. B. lower prices. C. lower output. D. None of these is true.
The barrier to entry protecting a social site like Facebook is primarily
A. economies of scale. B. ownership of a scarce factor of production. C. patents. D. network effects.