The nominal, effective exchange rate is the:
a. Nominal, effective exchange rate adjusted for a nation's price level relative to many foreign countries' prices.
b. Value of one currency in terms of another currency.
c. Weighted-average value of a currency relative to many foreign currencies.
d. Nominal, bilateral exchange rate adjusted for the international price levels of the two countries.
.C
You might also like to view...
With regard to international trade,
A. Some countries do not have a comparative advantage in producing anything. B. The market mechanism determines the terms of trade. C. Rich countries benefit at the expense of poor countries. D. The production possibilities exceed the consumption possibilities.
Explain the effects of expansionary monetary policy on a country's balance of payments and real product and income with floating exchange rates.
What will be an ideal response?
The U.S. Social Security tax is an example of a
A) progressive tax. B) proportional tax. C) premium tax. D) regressive tax.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.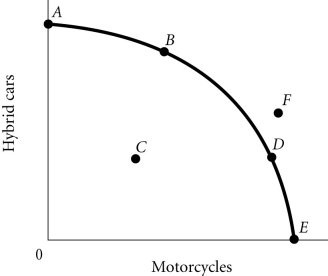 Figure 2.4Refer to Figure 2.4. The economy moves from Point E to Point B. This could be explained by
Figure 2.4Refer to Figure 2.4. The economy moves from Point E to Point B. This could be explained by
A. a change in society's preferences for hybrid cars versus motorcycles. B. an increase in economic growth. C. an increase in unemployment. D. a reduction in unemployment.