In Figure 45.1, the opportunity cost to workers of working at the equilibrium wage-labor combination is 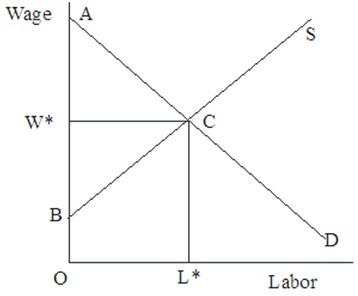 Figure 45.1
Figure 45.1
A. OW*CL*.
B. ABC.
C. OBCL*.
D. OACL*.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The size of the deadweight loss, or excess burden, of a tax depends on the
A) amount of producer surplus but not the amount of consumer surplus because it is the producers who send the tax revenues to the government. B) strength of demand. C) strength of supply. D) elasticities of demand and supply. E) number of demanders and the number of suppliers.
Burning coal to generate electricity can create pollution. If the market for generating electricity is competitive and is allowed to operate without any government intervention, is the equilibrium quantity of coal burned equal to, more than, or less
than the efficient quantity?
From the manager's perspective:
A) it is important to treat implicit costs as explicit in order to make sound strategic decisions. B) implicit costs are simply a theoretical construct and should be ignored in the decision-making process. C) only explicit costs matter because accounting profit is based on explicit costs. D) there is no difference between implicit and explicit costs. As such, treating implicit costs as explicit would result in double counting and an overstatement of total costs.
Which of the following is correct?
A. Policy lags are normally much shorter for fiscal policy than for monetary policy. B. Congress usually makes major fiscal policy changes in a fairly short period of time. C. Expenditure lags are much longer for investment, the main way in which monetary policy affects aggregate demand. D. Monetary policy affects aggregate demand more quickly than fiscal policy, such as tax or government spending changes.