While the gondola is rising at a speed of 5.0 m/s, a passenger in a balloon-supported gondola throws a small ball up at a speed of 2.0 m/s relative to his body. A person who measures the ball's velocity at the instant of release will find that the ball's velocity relative to the ground at that instant is
a. 2.0 m/s, up.
b. 2.8 m/s, down.
c. 3.0 m/s, up.
d. 5.0 m/s, up.
e. 7.0 m/s, up.
e
You might also like to view...
Polarization: As shown in the figure, the orientation of the transmission axis for each of three ideal polarizing sheets is labeled relative to the vertical direction. A beam of light, polarized in the vertical direction, is incident on the first polarizer with an intensity of 1.00 kW/m2. What is the intensity of the beam after it has passed through the three polarizing sheets when ?1 = 30°, ?2 = 30°, and ?3= 60°?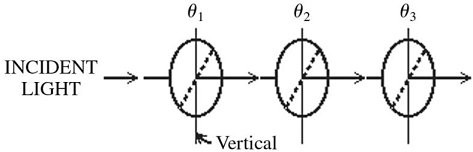
A. 141 W/m2 B. 316 W/m2 C. 433 W/m2 D. 563 W/m2 E. 188 W/m2
Waves on a String: A rope with a total mass of 25.0 kg is tied to a tree on one side of a 125-m wide ravine. You are pulling on the other end of the rope with a force of 415 N. If you pluck the rope at your end, how long will it take the pulse to travel across the ravine to the tree?
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
What is the origin of the lobes often observed on opposite sides of radio galaxies?
A. black holes orbiting the center B. high-speed electrons spiraling around magnetic field lines C. supernovae from massive stars D. gas ejected from the core of the galaxy E. hot planetary nebulas surrounding the galaxy
This curve shows the distribution of atomic speeds calculated from an experiment in which particles of gas are projected through an apparatus as shown on page 217 of your textbook. How would the distribution of speeds change if the temperature of the gas were increased?
a. The shape of the distribution would remain qualitatively the same, but would shift to the right. b. Same as answer a., except that the shift is to the left. c. The distribution is not affected by temperature. d. The peak gets higher without shifting over while the height of other parts of the curve decreases. e. The peak gets lower without shifting over while the height of other parts of the curve increases.