Helen is a 19-year-old single mother of two. She has no car and works at a minimum wage job. She receives some assistance from the government, but every time she earns $1, she loses $1 in government assistance. Helen is caught in the poverty trap, which means that:
a. she is taxed at the higher poverty-line rate.
b. making more money does not lead to having more money.
c. because she accepts government assistance, she is getting lazier.
d. unless she continues to work, her children will go into foster care.
b. making more money does not lead to having more money.
The poverty trap results from antipoverty programs set up so that government benefits decline substantially as people earn more income—as a result, working provides little financial gain.
You might also like to view...
In an indifference curve/budget line diagram, at your consumer equilibrium, that is, your best affordable point, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Any movement upward or downward on your budget line will move you to a less preferred point. B) Any movement upward or downward on your indifference curve will move you to a less preferred point. C) Your marginal rate of substitution is greater than the magnitude of the budget line by as much as possible. D) All of the above are correct.
In a simplified system where all banks have uniform reserve requirements and checkable deposits are the only form of money, the money multiplier is equal to 1 over the required reserve ratio
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Producer surplus is always the total area below the price and above the supply curve
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
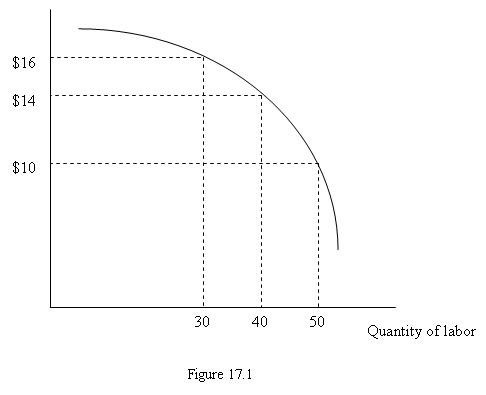 Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage increases:
Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage increases:
A. the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward. B. the marginal revenue product curve shifts downward. C. the marginal revenue product curve does not shift, but there is a movement upward along the curve. D. the marginal revenue product curve does not shift, but there is a movement downward along the curve.