In a typical graph for a purely competitive firm, at the point where the total cost and total revenue curves intersect, the firm:
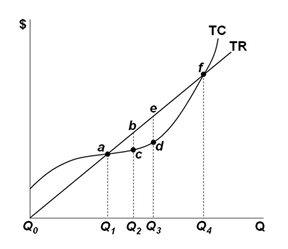
A. Earns some economic profit
B. Suffers some economic loss
C. Earns some normal profit
D. Suffers some accounting loss
C. Earns some normal profit
You might also like to view...
With a natural monopoly, the normal profit price is ________ and the competitive price is ________.
A. not allocatively efficient; allocatively efficient B. allocatively efficient; allocatively efficient C. not allocatively efficient; not allocatively efficient D. allocatively efficient; not allocatively efficient
The preceding table gives monthly production information for Peter's Peanuts, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. The market price of peanuts is $2.00 per pound
If a worker costs $800 per month, how many workers will Peter employ to maximize profit? A) zero B) one C) two D) four
When economic profits are negative, accounting profits
A) must be positive. B) will be negative. C) will equal zero. D) could be positive, negative or zero.
 Table 15.1Table 15.1 shows the preferred budget in millions for a new sports facility and the number of thousands of voters in a community who prefer that budget. What budget does the median voter prefer?
Table 15.1Table 15.1 shows the preferred budget in millions for a new sports facility and the number of thousands of voters in a community who prefer that budget. What budget does the median voter prefer?
A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6