Refer to the diagrams for two separate product markets. Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q 0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S 1 in diagram (a) on the left and from S to S 2 in
diagram (b) on the right. The shift of the supply curve from S to S 2 in diagram (b) might be caused by a per-unit:
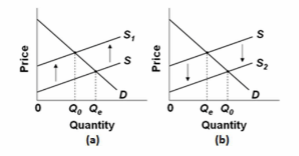
A. subsidy paid to the producers of this product.
B. tax on the producers of this product.
C. subsidy paid to the buyers of this product.
D. tax on the buyers of this product.
A. subsidy paid to the producers of this product.
You might also like to view...
Lucky buys hats for $20 but Lucky will not sell one of her hats for less than $35. Lucky is ________
A) displaying the endowment effect B) making decisions using her prefrontal cortex C) exhibiting bounded self-interest D) showing unbounded will power
In the above figure, Brendan originally consumes at point A. If his income falls and compact discs are a normal good but haircuts are an inferior good then he will begin consuming at a point such as
A) B. B) E. C) F. D) G.
If a firm expects that the price of its product will be lower in the future than it is today
A) the firm has an incentive to decrease supply now and increase supply in the future. B) the firm will not change supply until it knows for certain what will happen to its price. C) the firm has an incentive to increase quantity supplied now and decrease quantity supplied in the future. D) the firm has an incentive to increase supply now and decrease supply in the future.
If the central bank pursues a monetary policy that is more expansionary than what firms and people expect, then the central bank must be trying to
A) boost output in the short run. B) constrain output in the short run. C) constrain prices. D) boost prices in the short run.