As the U.S. dollar appreciates against foreign currencies, the U.S. ____________ curve shifts _____________ resulting in a(n) _________________ in the U.S. price level and a(n) _________________ in Real GDP in the United States
A) AD; leftward; decrease; decrease
B) AD; rightward; increase; increase
C) SRAS; rightward; decrease; increase
D) SRAS; leftward; increase; decrease
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The basis for both first-degree price discrimination and third-degree price discrimination is differences in the buyers' willingness to pay for a good. B) The basis for both first-degree price discrimination and third-degree price discrimination is differences in the sellers' willingness to accept payment for a good. C) The basis for first-degree price discrimination is differences in willingness to pay, whereas the basis for third-degree price discrimination is differences in the sellers' willingness to accept payment for a good. D) The basis for first-degree price discrimination is differences in the seller's willingness to accept payment for a good, whereas the basis for third-degree price discrimination is differences in buyers' willingness to pay for a good.
An increase in supply will occur when
A) the supply curve shifts downward to the right. B) the supply curve shifts upward to the left. C) the demand curve shifts downward to the left. D) the demand curve shifts upward to the right.
Suppose the price of one share of a particular stock fell from $26.25 to $24.75 over the course of a year, and the stock paid a dividend of $0.90 per share during the same year. What was the total return on the share of stock?
A. 9.1 percent B. 2.4 percent C. ?5.7 percent D. ?2.3 percent
Refer to the data provided in Table 9.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 9.1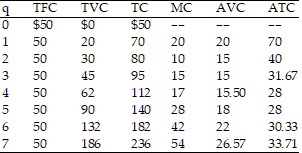 Refer to Table 9.1. If the market price is $17, then in the short run the firm will
Refer to Table 9.1. If the market price is $17, then in the short run the firm will
A. operate and expand. B. operate but not expand. C. shut down, but not go out of business. D. go out of business.