Calculating the value of an economy is more complex than just adding up the value of every single thing that is produced because that would lead to:
A. overcounting, as there is a mark-up in everything that is sold.
B. undercounting, as only observable markets can be recorded.
C. overcounting, as the value of intermediate products would be counted twice.
D. undercounting, as most goods are not sold in retail markets.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the above figure, point B represents
A) a recessionary gap. B) a full-employment equilibrium. C) an inflationary gap. D) a decrease in aggregate demand.
Use the above table. The income elasticity of artisan bread is
A) 1.285. B) 0.780. C) 0.012. D) 8.330.
This table shows individual demand schedules for a market.
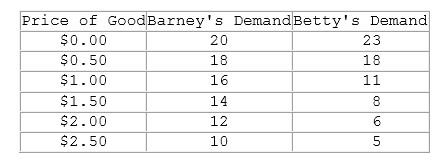
According to the table shown, at a price of $1.00, how much of the good will be demanded by Betty?
A. 16
B. 11
C. 46
D. 30
The faster the rate of technological progress: a. the greater the rate of economic growth
b. the slower the rate of economic growth. c. the greater the rate of population growth. d. the slower the rate of growth of the money supply.