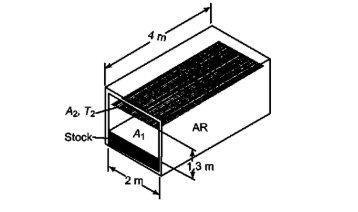
An electric furnace is to be used for batch heating a certain material with specific heat of 670 J/(kg K) from 20 to 760°C. The material is placed on the furnace floor which is 2m x 4m in area as shown in the accompanying sketch. The side walls of the furnace are made of a refractory material. Parallel to the plane of the roof, but several inches below it, a grid of round resistor rods is installed. The resistors are 13 mm in diameter and are spaced 5 cm center to center. The resistor temperature is to be maintained at 1100°C, under these conditions the emissivity of the resistor surface is 0.6. If the top surface of the stock is assumed to have an emissivity of 0.9, estimate the time required for heating a 6 metric ton batch. External heat losses from the furnace may be neglected, the
temperature gradient through the stock can be considered negligibly small, and steady-state conditions can be assumed.
GIVEN
- Batch heating of material in the furnace shown above
- Specific heat of material (c) = 670 Jkg K
- Material temperatures
- Initial 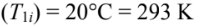
- Final 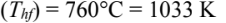
- Furnace dimensions: 2 m x 4 m x 1.3 m high
- Side walls are refractory material
- Resistor rod diameter (Dr) = 13 mm = 0.013 m
- Resistor center to center distance (s) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
- Resistor temperature (T2) = 1100°C = 1373 K
- Emissivity of the resistor surface (?2) = 0.6
- Emissivity of the material surface (?1) = 0.9
- Mass of material (m) = 6 metric tons = 6000 kg
FIND
- The time required (t) for heating the 6 metric ton batch
ASSUMPTIONS
- Quasi-steady state conditions
- External heat losses are negligible
- Temperature gradient through the material is negligible (negligible internal thermal resistance)
- Material is gray
- Convective heat transfer is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 x 10–8 W/(m2 K4
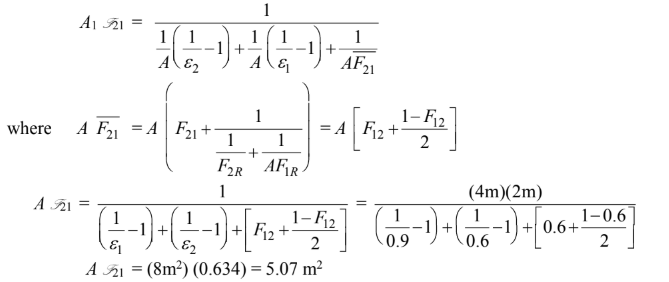
The shape factor F21 can be read off. For s/D = 50/13 = 3.85 and one row: F21 = 0.60.
Note that A1 = A2, therefore, F21 = F12.
The sum of the shape factors from a given surface must sum to unity
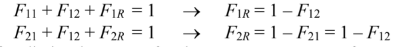
The rate of radiative heat transfer, between two gray surfaces connected by re-radiating surfaces is
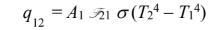
where A2 f21 is note that A1 = A2 = A
The temperature changes in the material is given by
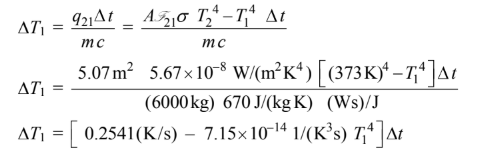
As T1 increases, the rate of heat transfer will decrease. Therefore, the equation above will be solved for
a chosen time increment and the temperature T1 will then be updated. This procedure will be repeated
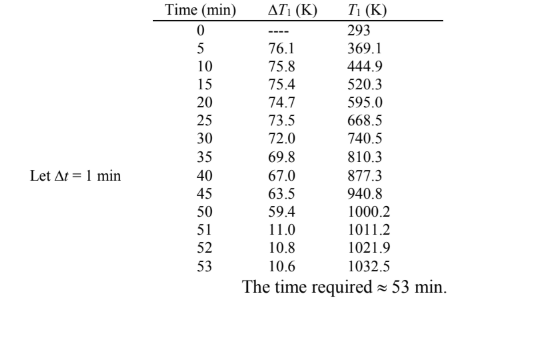
until T1 = 760°C = 1033 K.
Let ?t = 5 min = 300 s initially
You might also like to view...
A steam generator is a device that converts water into steam by capturing radiant heat from hot gases. Consider a 15 foot cubed steam generator, all sides made up of water tubes and a “fire ball” 6 ft. in diameter at 4000ºF at the center. If the water tubes have a surface temperature of 600ºF and an emissivity of 0.7, determine the heat transfer to the water from the combustion gases. Assume the fire ball acts as a black body.
What will be an ideal response?
A hidden link that looks like body text until point to it, at which time it changes color is a(n) ______ link.
A. hot spot B. formatted C. image D. rollover
The fast rotation of neutron stars is a consequence of the law of conservation of angular momentum.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
An automobile manufacturer claims that its product will, starting from rest, travel 0.40 km in 9.0 s. What is the magnitude of the constant acceleration required to do this?
a. 9.9 m/s2 b. 8.9 m/s2 c. 6.6 m/s2 d. 5.6 m/s2 e. 4.6 m/s2