The rate at which the concentration of a drug in the bloodstream decreases is proportional to the concentration at any time t. Initially, the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream is B0 g/mL. What is the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream at any time t? Formulate but do not solve the problem in terms of a differential equation with a side condition.
What will be an ideal response?
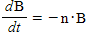 ;
; 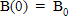
Mathematics
You might also like to view...
Factor by grouping.12x4 + 8x2 - 9x2 - 6
A. (4x4 - 3)(3x + 2) B. (4x2 + 3)(3x2 - 2) C. (4x2 - 3)(3x2 + 2) D. (12x2 + 3)(x2 - 2)
Mathematics
Solve the problem.Find the approximate area bounded by 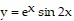 , x = 0,
, x = 0, 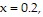 and the
and the 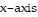 by using the first three nonzero terms of the appropriate series.
by using the first three nonzero terms of the appropriate series.
A. 0.47467 B. 0.48267 C. 0.43733 D. 0.04520
Mathematics
Provide an appropriate response.The annual interest paid on a bond is equal to the face value of the bond:
A. multiplied by the stated annual interest rate B. plus the stated annual interest rate C. minus the stated annual interest rate D. divided by the stated annual interest rate
Mathematics
Simplify using scientific notation. Express the answer in standard notation.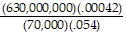
A. .07 B. 7 C. .007 D. 70
Mathematics