How does digestion occur in the large intestine?
A) The mucosa of the large intestine produces enzymes that begin digestion.
B) Pancreatic juice flows through the pancreatic duct into the large intestine allowing digestion to occur.
C) Bile enters the large intestine through the bile duct.
D) No digestive enzymes are produced in the large intestine but digestion continues from the enzymes present that were secreted or produced in the small intestine.
E) No digestive enzymes are produced and the digestive enzymes from the small intestine are inactivated in the large intestine so digestion does not occur in the large intestine.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The thoracic cavity lies ________the abdominopelvic cavity.
A. superior to B. inferior to C. dorsal (posterior) to D. ventral (anterior) to
Using the figure above, identify the labeled part.
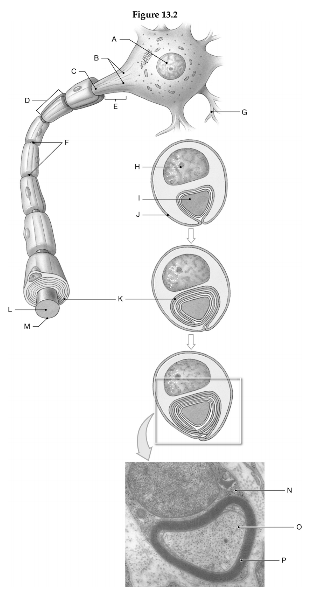
1. Label A: ______________________________
2. Label B: ______________________________
3. Label C: ______________________________
4. Label D: ______________________________
5. Label E: ______________________________
6. Label F: ______________________________
7. Label G: ______________________________
8. Label H: ______________________________
9. Label I: ______________________________
10. Label J: ______________________________
11. Label K: ______________________________
12. Label L: ______________________________
13. Label M: ______________________________
14. Label N: ______________________________
15. Label O: ______________________________
16. Label P: ______________________________
In the sarcomere the protein that forms two twisted strands around a central rod-like protein is called
A) titin B) actin C) G actin D) nebulin E) myosin
Describe lipids in terms of their elemental composition and solubility in water
A) water-soluble organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen B) water-insoluble organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen C) water-soluble inorganic compounds made up of hydrogen and oxygen D) water-insoluble inorganic compounds made up of hydrogen and oxygen E) water-soluble organic compounds made up of hydrogen and oxygen