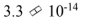A mass of 2 kg traveling at 3 m/s undergoes a one-dimensional elastic collision with a group of four 1-kg masses that are at rest in contact with each other and lined up in the same direction as the velocity of the 2-kg mass
As a result of the collision A)
the 2-kg mass comes to a stop and one of the 1-kg masses takes off at 6 m/s.
B)
the 2-kg mass comes to a stop and two of the 1-kg masses take off at 3 m/s.
C)
the 2-kg mass comes to a stop and three of the 1-kg masses take off at 2 m/s.
D)
the 2-kg mass comes to a stop and all four of the 1-kg masses take off at 2 m/s.
E)
the 2-kg mass and the five other masses travel at 1 m/s.
B
You might also like to view...
X-rays come from certain regions of the interstellar medium because gas molecules in those regions are at a very high density
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
If you release a single molecule in an evacuated region it will initially
A) fall just as a baseball would. B) move in any direction. C) convect upward. D) be buoyed upward. E) none of the above
Monochromatic light shines on a surface with work function 1.80 eV. The maximum energy of the emitted photoelectrons is 0.620 eV. What is the wavelength of the monochromatic light?
A. 200 nm B. 290 nm C. 689 nm D. 602 nm E. 512 nm
Two cars are traveling down the highway in the same direction. Car A is traveling at 30.0 m/s and car B is passing car A at a relative speed of 3.0 m/s. Using Galilean relativity to calculate the speed of car B relative to the highway results in an answer incorrect by how many m/s?
a. 
b. 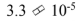
c. 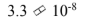
d. 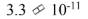
e.