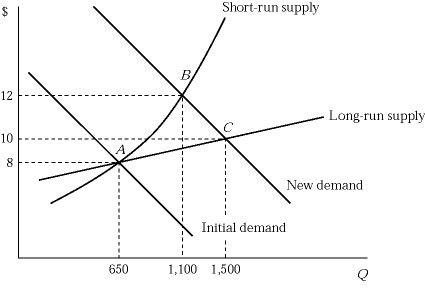
 Figure 6.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. Suppose that the market demand curve shifts to the right. Why is the short-run supply curve steeper than the long-run supply curve?
Figure 6.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. Suppose that the market demand curve shifts to the right. Why is the short-run supply curve steeper than the long-run supply curve?
A. Because production facilities are fixed in the short run.
B. Because each firm experiences diminishing returns in the short run.
C. Because production becomes costlier as firms squeeze more output from the existing production facilities.
D. All of these are correct.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Government price controls a. strip market prices of their ability to signal relative scarcities to both buyers and sellers. b. often impose harm on at least some of the group of people they are trying to assist. c. sometimes force prices above or below what they would be in a market economy
d. all of the above
Marginal product is:
A. the output of the least skilled worker. B. a worker's output multiplied by the price at which each unit can be sold. C. the amount an additional worker adds to the firm's total output. D. the amount any given worker contributes to the firm's total revenue.
If a firm perceived that the other firm in an implicit pricing agreement dropped its price in response to a change in market conditions, then its most likely response would be to:
A. match the other firm's price. B. engage in a price war. C. raise price to punish the other firm. D. keep its price the same.
Behavioral economists criticize neoclassical models as being:
A. Messy and imprecise B. Accurate but artificially elegant C. Precise but inaccurate D. Vague but accurate