There are no tides to be seen in the community swimming pool because
A) gravitation on the small mass of water is negligibly small.
B) it is shallow compared to the ocean.
C) all parts of it are practically the same distance from the Moon.
D) they are masked by the much stronger pull of Earth's gravity.
E) But there are, at nighttime.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Silver solder
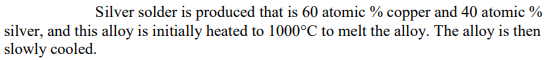
(a) At what temperature does the first solid form, and what is the chemical composition of this first solid to form?
(b) At what temperature does the alloy completely transform to a solid; what phases are present after the alloy is completely solid, and what are their chemical compositions at the transformation temperature?
(c) At room temperature, what is the atom fraction of each phase present?
Why does the Cepheid "standard candle" have limited usefulness beyond 20 Mpc?
A) Distant galaxies are seen in the past, when Cepheid variables behaved differently than they do today. B) Distant galaxies are so young they do not contain Cepheids. C) Cepheids are too faint to be seen beyond that distance, even with HST. D) The light variability of Cepheids diminishes with distance so they do not appear to vary there. E) Older distant Cepheids are of Population II, where the period-luminosity relation no longer works.
Observations show that elements with atomic mass numbers divisible by 4 (such as oxygen-16, neon-20, and magnesium-24 ) tend to be more abundant in the universe than elements with atomic mass numbers in between. Why do we think this is the case?
A) The apparent pattern is thought to be a random coincidence. B) Elements with atomic mass numbers divisible by 4 tend to be more stable than elements in between. C) At the end of a high-mass star's life, it produces new elements through a series of helium capture reactions. D) This pattern in elemental abundances was apparently determined during the first few minutes after the Big Bang.
What is the "runaway greenhouse effect"?
What will be an ideal response?