An object starts from rest with an acceleration of 2.0 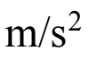 for 3.0 seconds. It then reduces its acceleration to 1.0 m/s2 for 5.0 additional seconds. The velocity at the end of the 5.0 seconds interval is
for 3.0 seconds. It then reduces its acceleration to 1.0 m/s2 for 5.0 additional seconds. The velocity at the end of the 5.0 seconds interval is
A. 6.0 m/s.
B. 18 m/s.
C. 8.0 m/s.
D. 18 m/s.
E. 11 m/s.
E. 11 m/s.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A: For an observer located in a galaxy all other distant galaxies would appear to move away from his. B: The universe looks the same in all directions; i.e. it is homogeneous and isotropic. C: The universe is expanding. D: In our universe, at earlier times, everything was closer together. E: We are at the center of the universe.
Our whole galaxy is about ____ times larger in size.
A.) 100. B.) 1,000. C.) 10,000. D.) 100,000. E.) 1,000,000.
Compared to the Earth, the Moon is no longer geologically active because
a. it is rotating too slowly. b. its radioactive elements were never abundant. c. it is much smaller in mass. d. its crust is too thin. e. it does not have water on its surface.
On planet X, the absolute pressure at a depth of 2.00 m below the surface of a liquid nitrogen lake is 5.00 × 105 N/m2. At a depth 5.00 m below the surface, the absolute pressure is 8.00 × 105 N/m2. The density of liquid nitrogen is 808 kg/m3
(a) What is the atmospheric pressure on planet X? (b) What is the acceleration due to gravity on planet X? What will be an ideal response?