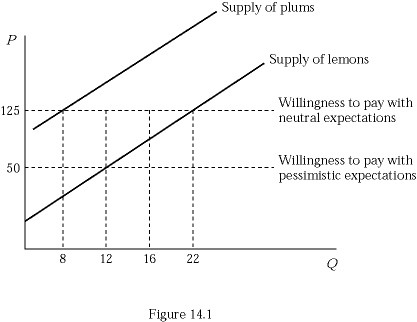
 Figure 14.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer bikes are sold in equilibrium?
Figure 14.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer bikes are sold in equilibrium?
A. 8
B. 12
C. 18
D. 22
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Classical growth theory predicts that increases in real GDP per person will
A) last because people make choices in the pursuit of higher profits. B) not last because higher income encourages smaller families and a lower population growth rate. C) not last because higher income leads to a population explosion. D) last because higher growth leads to new technology. E) last only if the government directs firms to make more investments in capital and new technology.
A firm has excess capacity if its output is
A) less than the quantity at which marginal cost is minimized. B) less than the quantity at which economic profit is maximized. C) less than the quantity at which average total cost is minimized. D) more than the quantity at which average total cost is minimized.
Economists often refer to taxes, subsidies, legal rules, and public auctions as methods of indirect regulation. Explain what this means and what are its limitations
What will be an ideal response?
In China
A) wages are beginning to rise, reducing its comparative advantage. B) there is little advantage from scale economies. C) the middle class is not expanding. D) poor coastal areas limit trade.