In the diagram below, the importance of the erupting volcano at "B" for the global carbon cycle is that
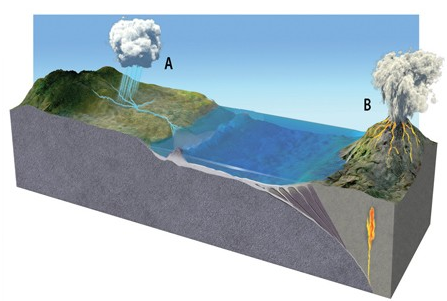
A) CO2 dissolved in magma rises with the magma and is released from solution into the atmosphere as pressures decrease, warming the Earth.
B) the heat from the erupting volcano warms the atmosphere to such an extent that it can no longer retain CO2 in it, causing it to condense and cool the Earth.
C) as the magma begins to cool when it reaches the surface, atmospheric CO2 is absorbed into it, cooling the Earth.
D) atmospheric CO2 gets drawn into the volcanic caldera as soon as the magma exits the chamber, cooling the Earth.
A) CO2 dissolved in magma rises with the magma and is released from solution into the atmosphere as pressures decrease, warming the Earth.
You might also like to view...
Exfoliation domes are formed from which of the following processes?
A) sheeting B) oxidation C) melting D) metamorphism
The indigenous Mãori people refer to New Zealand as:
A) Aotearoa B) Mao-Mao C) Pago-Pago D) Diprotodon
Which of the following is true in naming ketones?
A) The root name is based on the longest carbon chain which contains the carbonyl carbon. B) The oxygen atom is always bonded to C-1. C) both a and b D) neither a nor b
The movement of a glacier is normally measured in ________ per day
A) centimeters (inches) B) meters (feet) C) tens of meters (tens of feet) D) kilometers (miles) E) tens of kilometers (tens of miles)