A heat engine has an efficiency of 35.0% and receives 150 J of heat per cycle
(a) How much work does it do in each cycle?
(b) How much heat does it "waste" in each cycle?
What will be an ideal response?
(a) 52.5 J (b) 97.5 J
You might also like to view...
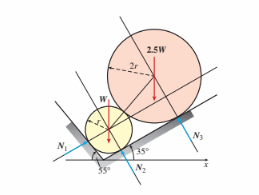
Two cylinders are in contact along an inclined plane. The upper cylinder (weight is 2.5W) rests against the lower cylinder (weight W), and both are supported by a wall where the contact force is N1. Assume that all friction forces are negligible. An expression for contact force N1 in terms of load variable W is:
(A) 1.75W
(B) 3.5W
(C) 1.57W
(D) 2.01W
Which of the following is the most basic definition of a greenhouse gas?
A) a gas that reflects a lot of sunlight B) a gas that keeps warms air from rising, and therefore warms the surface C) a gas that absorbs infrared light D) a gas that makes a planet much hotter than it would be otherwise, even in small amounts
An unfueled 1000-kg experimental rocket sled at rest on level frictionless rails is loaded with 50 kg of propellant. It exhausts the propellant in a 20 s "burn.". The rocket moves at 160 m/s after the burn. What average force is experienced by the rocket during the burn?
a. 0.80 × 10^4 N b. 0.75 × 10^4 N c. 0.60 × 10^4 N d. 0.35 × 10^4 N
The objective and the eyepiece of a microscope have focal lengths of 4.00 mm and 25.0 mm, respectively
The objective produces a real image 30 times the size of the object. The final image is viewed at infinity, and the near point of the microscope user is at 25.0 cm. What is the distance between the object and the focal point of the objective? A) 0.13 mm B) 0.18 mm C) 0.23 mm D) 0.28 mm E) 0.33 mm