The flattening of a spherical body, usually caused by rotation, is referred to as__________
A) oblateness
B) occultation
C) collimation
D) waning
A
You might also like to view...
Compound Microscope: The focal lengths of the objective lens and the eyepiece of a microscope are 0.50 cm and 2.0 cm, respectively, and their separation is 6.0 cm when adjusted for minimum eyestrain for a person with a near point of 25.0 cm. If the microscope is focused on a small object, the magnitude of its final overall magnification is closest to
A. 50. B. 100. C. 150. D. 200. E. 250.
A speeding car traveling at a constant velocity of 24 m/s passes a police care initially at rest beside the roadway. If the police car with constant acceleration of 3.0 m/s2 immediately pursues the speeding car, how far down the road does it draw even with the speeding car?
a. 190 m b. 290 m c. 380 m d. 770 m
The color of an object depends on the colors of
A) the light that illuminates them. B) molecules that comprise them. C) the foreground.
The horizontal surface on which the objects slide is frictionless. If M = 2.0 kg, the tension in string 1 is 12 N. Determine F
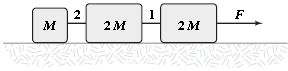
a.
25 N
b.
20 N
c.
30 N
d.
35 N
e.
40 N