A battery has an emf of 12.0 V and an internal resistance of 3.00 ?. If the battery delivers 120 mA when connected to a load, what is the load resistance?
a. 97.0 ?
b. 100 ?
c. 4.00 ?
d. 36.0 ?
a
You might also like to view...
A conducting sphere of radius 10.0 cm holds a net charge of 4.4 ?C. What is the surface charge density?
A. 0.0
B. 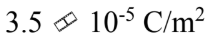
C. 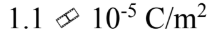
D. 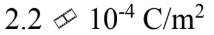
E. 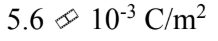
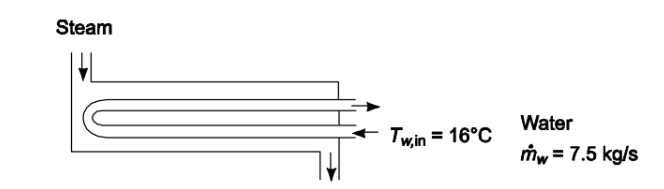
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger with the characteristics given below is to be used to heat 27,000 kg/h of water before it is sent to a reaction system. Saturated steam at 239 kPa absolute pressure is available as the heating medium and will be condensed without subcooling on the outside of the tubes. From previous experience, the steam-side condensing coefficient can be assumed constant and equal to 11,300 W/(m2 K). If the water enters at 16°C, at what temperature will it leave the exchanger? Use reasonable estimates for fouling coefficients. Exchanger specifications
- Tubes – 2.5-cm-OD, 2.3-cm-ID, horizontal copper tubes in six vertical rows
- Tube length = 2.4 m
- Total number of tubes = 52
- Number of tube-side passes = 2
GIVEN
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger - water in copper tubes, saturated steam is shell Water flow rate m w= 27,000 kg/h = 7.5 kg/s Steam pressure = 2.36 atm = 239 kPa Steam-side coefficient h o= 11,300 W/(m2 K) Water entrance temperature: Tw,in = 16°C Tube diameters
? Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
? Di = 2.3 cm = 0.023 m Tube length (L) = 2.4 m Number of tubes (N) = 52 Number of tube passes = 2
FIND
The water exit temperature (Tw,out)
ASSUMPTIONS
Length given is total tube length for both passes
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the temperature of saturated steam at 239 kPa (Ta) = 125°C
for water at 20°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.597 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 1.006 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 7.0 Density (?) = 998.2 kg/m3 Specific heat (cp) = 4182 J/(kg K), the thermal conductivity of copper (kc) = 392 W/(m K) at 127°C
The ratio of the density of a material to the density of water is
a. the mass density. b. the weight density. c. the specific gravity. d. the buoyant force. e. none of the above.
An image formed when the light rays pass through the image location, and could appear on paper or film placed at that location is referred to as a(n)
A) real image. B) virtual image. C) imaginary image. D) positive image. E) negative image.