An object 4.0 cm in height is placed 8.0 cm in front of a concave spherical mirror with a focal length of 10.0 cm. What is the position of its image in relation to the mirror, and what are the characteristics of the image?
A) 10.0 cm on the same side of mirror, real, 6.0 times bigger
B) 10.0 cm on the other side of mirror, virtual, 10.0 times bigger
C) 40.0 cm on the other side of mirror, real, 6.0 times bigger
D) 40.0 cm on the other side of mirror, virtual, 5.0 times bigger
E) 18.0 cm on the same side of mirror, virtual, 2.25 times bigger
D
You might also like to view...
Interference: What do we mean when we say that two light rays striking a screen are in phase with each other?
A. When the electric field due to one is a maximum, the electric field due to the other is also a maximum, and this relation is maintained as time passes. B. They are traveling at the same speed. C. They have the same wavelength. D. They alternately reinforce and cancel each other.
What is the direction of 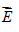 in the wave as it passes S?
in the wave as it passes S?
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. Toward the viewer. F. Away from the viewer. T. The vector is zero. G. AA H. BB I. CC J. DD
A light ray enters a glass enclosed fishtank. From air it enters the glass at 20.° with respect to the surface, then emerges into the water. The index for glass is 1.50 and for water 1.33
(a) What is the angle of refraction in the glass? (b) What is the angle of refraction in the water? (c) Is there any incident angle in air for which the ray will not enter the water due to total internal reflection?
Which of the following is a conservative force? (All refer to a car on a slope.)
a. The force you exert on the car pushing it uphill. b. The force exerted by rain drops falling on the car. c. The frictional force of the road on the car. d. The gravitational force acting on the car. e. The force you exert on the car (pushing it uphill) after it starts to slide downhill.