Virus infected cells and tumor cells are targeted by ________, which are lymphoid derived cells of the innate immunity
a. cytotoxic T cells
b. neutrophils
c. plasma cells
d. natural killer cells
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The figure below shows results of bristle number in Drosophila flies after 35 generations of artificial selection. This figure suggests that
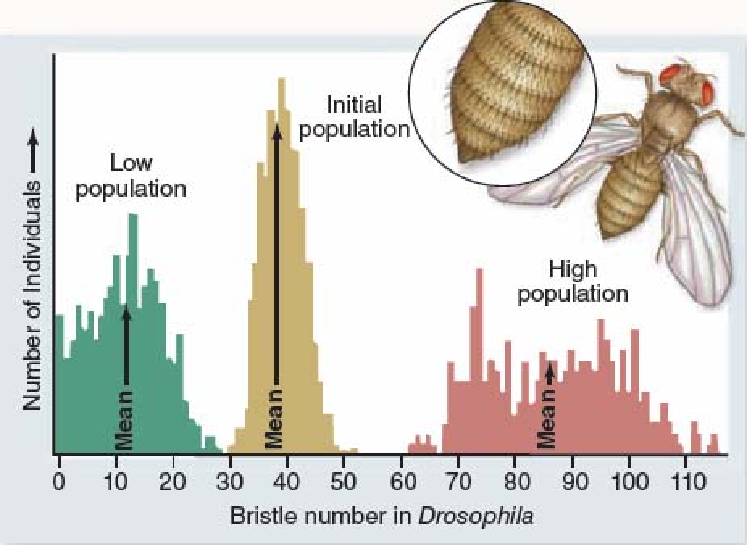
A. bristle number has evolved beyond the original range of phenotypic variation for this trait.
B. after 35 generations of selection, populations no longer exhibit variation in bristle number.
C. natural selection cannot lead to large phenotypic changes.
D. at the end of the experiment, "high population" flies were unable to interbreed with "low population" flies.
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content
What do you already know about artificial selection? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
What can be said about sex-determination in humans?
a. All human sperm carry a Y chromosome. b. 25% of human zygotes are XY. c. All zygotes carry a Y chromosome. d. Sex depends upon which type of sperm fertilizes the egg. e. All human eggs carry a Y chromosome.
What observation did Dr. Katsusaburo Yamagiwa make to lead him to believe that chemicals cause cancer?
A. He observed that cancer rates were 40 times higher in smokers than in nonsmokers. B. He observed that when coal tar extracts were applied to rabbit skin, cancers eventually developed. C. He observed that chimney sweeps exhibited frequent cancer of the scrotum. D. He observed unusual tumors of the nose in snuff users and suggested tobacco as the cause.
Insects that lay eggs in or on another insect, called ____________, are often used in biological pest control.
A. parasitoids B. brood parasites C. commensal insects D. invaders E. hymenopterans