Unconventional policy tools are useful when:
A. conventional policy tools result in shifts in the economy that are too large.
B. restrictive monetary policy is necessary.
C. lowering the target interest rate to zero is not sufficient to stimulate the economy.
D. conventional policy tools support only growth in the economy.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. An economy in short-run equilibrium at point A has a(n) ________ gap. The gap could be eliminated by the self-correcting mechanism of the economy and eventually achieve long-run equilibrium at point ________ or the central bank could intervene with monetary easing establishing the long-run equilibrium at point ________. 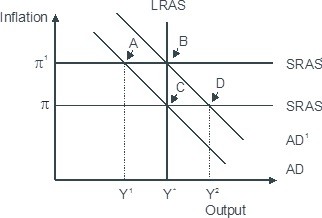
A. recessionary; B; C B. expansionary; B; C C. expansionary; C; B D. recessionary; C; B
Suppose that real GDP starts at 100 and grows at a rate of 10 percent per year for two years. In the third year real GDP would be
A) 110. B) 110.1. C) 120. D) 121.
Use a figure to illustrate the ineffectiveness of monetary policy to spur on an economy under a fixed exchange rate
What will be an ideal response?
During times of high unemployment, colleges often observe an increase in enrollment even if tuition remains unchanged. Why?
A. Students go to college even when the net benefit is negative. B. The opportunity cost of attending college is higher when unemployment is high. C. The benefit of attending college is lower because college graduates are less likely to find jobs. D. The opportunity cost of attending college is lower when unemployment is high.