Consider only the discriminant, b2 - 4ac, to determine whether one real-number solution, two different real-number solutions, or two different imaginary-number solutions exist.x2 - 6x + 4 = 0
A. Two different real-number solutions
B. One real solution
C. Two different imaginary-number solutions
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Expand and simplify the given expression by use of Pascal's triangle.(6x + 1)4
A. 1296x3 + 864x2 + 24x - 1 B. 1296x4 + 864x3 + 216x2 + 24x + 1 C. 1296x4 + 864x3 + 216x2 + 24x - 1 D. 1296x3 + 864x2 + 216x + 24
Give all possible rational zeros for the following polynomial.P(x) = 3x3 + 32x2 + 32x + 27
A. ±1, ± 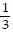 , ±
, ± 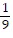 , ±
, ± 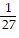 , ±3
, ±3
B. ±1, ± 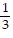 , ±3, ±9, ±27
, ±3, ±9, ±27
C. ±1, ±3, ±6, ±9, ±27
D. ±1, ±3, ±9, ±27
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand the binomial and express the result in simplified form.(x5 + 4y)4
A. x9 + 16x8y +24x7y2 + 16x5y3 + 4y4 B. x20 + 16x15y + 96x10y2 + 256x5y3 + 256y4 C. x20 + 12x15y + 96x10y2 + 192x5y3 + 256y4 D. x9 + 12x8y + 96x7y2 + 192x5y3 + 256y4
Use the commutative and associative properties to simplify the expression.-5(8y)
A. -40y B. 40y C. -40 + y D. 3y