When a star finally runs out of hydrogen to fuse in its central core
A) it grows smaller and dimmer, becoming a brown dwarf
B) it grows larger and brighter, becoming a giant or supergiant star
C) it grows smaller and dimmer becoming a white dwarf
D) it remains the same size but grows brighter
B
You might also like to view...
The redshifts of the galaxies imply that the Universe is expanding and that we are at the center
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
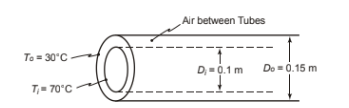
A solar collector design consists of several parallel tubes each enclosed concentrically in an outer tube that is transparent to solar radiation. The tubes are thin walled with the inner and outer cylinder diameters of of 0.10 and 0.15 m respectively. The annular space between the tubes is filled with air at atmospheric pressure. Under operating condition the inner and outer tube surface temperatures are 70°C and 30°C respectively.
(a) What is the convective heat loss per meter of tube length?
(b) If the emissivity of the outer surface of the inner tube is 0.2 and the outer cylinder
behaves as though it were a black body, estimate the radiation loss.
(c) Discuss design options for reducing the total heat loss.
GIVEN
? Thin walled concentric tubes with air atmospheric pressure between them
? Inner tube diameter (Di) = 0.1 m
? Outer tube diameter (Do) = 0.15 m
? Inner tube temperature (Ti) = 70°C = 343 K
? Outer tube temperature (To) = 30°C = 303 K
? Outer surface emissivity of inner tube (E) = 0.2
FIND
(a) The convective loss pe meter of tube (qc/L)
(b) The radiative loss (qr/L)
(c) Discuss design options for reducing the total heat loss
ASSUMPTIONS
? Steady state
? Tubes are horizontal
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS

Imagine that we place a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed positive charge Q and a particle with a negative charge -4Q as shown below. What are the directions of the total electric field vectors at the two points shown? 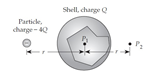 What is the direction at point P1 at the shell’s center?
What is the direction at point P1 at the shell’s center?
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. zero F. other G. AA H. BB I. CC J. DD
Earth's first atmosphere was rich in water vapor but poor in free oxygen. The atmosphere became more oxygenated with the
A) development of the ozone layer. B) emergence of stromatolites that developed a simple version of photosynthesis. C) emergence of gases from volcanic eruptions. D) both A and B.