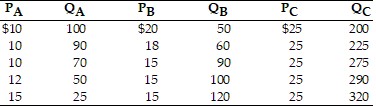
 Refer to the above table. The price of B decreases from $18 to $15. What is the cross price elasticity of demand between B and A?
Refer to the above table. The price of B decreases from $18 to $15. What is the cross price elasticity of demand between B and A?
A. -1.0
B. -0.73
C. +1.83
D. +1.38
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
An explanation for how the price of water can be less than the price of diamonds, even though water is more valuable, is that
a. price is a poor guide to value. b. markets for water and diamonds are not competitive. c. price reflects marginal value, not total value. d. diamond production requires more labor, and value is based on labor.
In the above figure, the maximum number of units that 4 workers can produce is
A) 5 units. B) 10 units. C) 15 units. D) more than 15 units.
In the short run, why would a firm in a perfectly competitive market shut down production if the prevailing market price falls below the lowest possible average variable cost?
a. At that point (economic) profit is zero. b. Below that point average revenue becomes less than marginal revenue. c. Below that point marginal revenue becomes insufficient to pay for avoidable average variable cost. d. Below that point other firms with similar cost will find it profitable to enter the market and take away demand from the existing firms.
If you purchase a good on credit, you are:
A. incurring a real liability to acquire a real asset. B. incurring a financial liability to acquire a real asset. C. exchanging a financial asset for another financial asset. D. exchanging a financial liability for a real liability.