If the price elasticity of supply is equal to zero and the price was to rise, the quantity supplied would:
A. decrease slightly.
B. fall to zero.
C. not change.
D. increase.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Recall the Application about the short-run and long-run elasticity of supply of coffee to answer the following question(s). Recall the Application. What is the reason identified in the Application regarding why the short-run elasticity of supply of coffee is more inelastic than in the long run?
A. It takes at least 3 years for a newly planted coffee bush to yield marketable beans. B. Coffee production is capital intensive, and the farmers cannot afford the additional capital. C. Fertilizers are expensive in countries that produce coffee. D. The government controls the supply of coffee in those countries.
Which of the following is NOT an economic function of the U.S. government?
A) promoting competition B) providing public goods C) promoting price stability D) encouraging production of government-inhibited goods
A farmer has many competitors and exists in a market structure known as perfect competition. This means that price is determined outside of the individual farmer's ability to charge a price higher than the going market for a bushel of wheat, hence the farmer is
A. a price maker and can therefore charge different customers different prices. B. never able to sell anything for any prices he charges. C. a price taker and cannot affect the market price of wheat. D. always able to price produce above the competition and earn a larger profit.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 3.18 below to answer the question(s) that follow.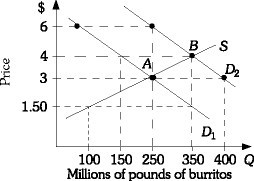 Figure 3.18Refer to Figure 3.18. The market is initially in equilibrium at Point A. If demand shifts from D1 to D2 and the price of burritos remains constant at $3.00, there will be
Figure 3.18Refer to Figure 3.18. The market is initially in equilibrium at Point A. If demand shifts from D1 to D2 and the price of burritos remains constant at $3.00, there will be
A. an excess supply of 150 million pounds of burritos. B. an excess demand of 100 million pounds of burritos. C. an excess supply of 50 million pounds of burritos. D. an excess demand of 150 million pounds of burritos.