The capital stock is fixed at 5 units, the price of capital is $60 per unit, and the price of labor is $20 per unit. 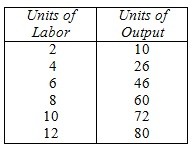 Based on the above, if the firm produces 60 units of output, what is average variable cost?
Based on the above, if the firm produces 60 units of output, what is average variable cost?
A. $2.67
B. $7.67
C. $20
D. $5
E. $57.50
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is Qd = 20,000 - 200P where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit maximizing output?
A. 2,000 B. 1,333.34 C. 1,000 D. 4,000
By the method of Lagrange multipliers, the optimal value of the Lagrange multiplier equals the:
A) marginal utility of income. B) marginal utility of each good. C) marginal utility per dollar spent on the last unit of each good. D) A and B above E) A and C above
Investment in a new facility is likely to increase the annual profit of a fertilizer producer by $85 . The producer will purchase the facility only if it requires an annual investment of $90
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The willingness and ability to buy specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
2. The pleasure or satisfaction obtained from a good or service. 3. The amount of satisfaction obtained from entire consumption of a product. 4. The change in total utility obtained by consuming one additional (marginal) unit of a good or service. 5. The marginal utility of a good declines as more of it is consumed in a given time period. 6. The assumption of nothing else changing. 7. The quantity of a good demanded in a given time period increases as its price falls, ceteris paribus. 8. A curve describing the quantities of a good a consumer is willing and able to buy at alternative prices in a given period, ceteris paribus. 9. Percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. 10. The price of a product multiplied by the quantity sold in a given time period. 11. A change in the quantity demanded at any (every) given price. 12. Percentage change in quantity demanded divided by percentage change in income. 13. Good for which demand increases when income rises. 14. Good for which demand decreases when income rises. 15. Goods that substitute for each other; when the price of good X rises, the demand for good Y increases, ceteris paribus. 16. The most desired goods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else. 17. Percentage change in quantity demanded of good Y divided by the percentage change in price of good X. 18. Goods frequently consumed in combination; when the price of good X rises, the demand for good Y falls, ceteris paribus. Demand Opportunity Cost Total Revenue Total Utility Ceteris Paribus Price Elasticity of Demand Marginal Utility Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Substitute Goods Shift in Demand Inferior Good Demand Curve Utility Income Elasticity of Demand Normal Good Complementary Goods Law of Demand Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand