The aggregate expenditures model and the aggregate demand curve can be reconciled because, other things equal, in the aggregate expenditures model:
A. changes in the price level have no effect on the equilibrium level of GDP.
B. an increase in the price level increases the real value of wealth.
C. the level of aggregate expenditures and therefore the level of real GDP vary inversely with
the price level.
D. the level of aggregate expenditures and therefore the level of real GDP vary directly with
the price level.
C. the level of aggregate expenditures and therefore the level of real GDP vary inversely with
the price level.
You might also like to view...
What are the four main ways in which the CPI is an upward-biased measure of the price level?
What will be an ideal response?
In the graph below, the price of capital is $500 per unit. Given a total cost of $50,000, the maximum amount of output possible is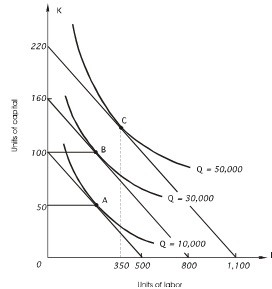
A. 1,100 units of output. B. 500 units of output. C. 10,000 units of output. D. 50,000 units of output. E. none of the above
Strategic decision making is most important in:
A. oligopolistic markets. B. monopolistically competitive markets. C. competitive markets. D. monopolistic markets.
Refer to the diagram. This economy will experience unemployment if it produces at point:
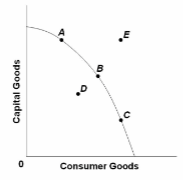
A. A.
B. B.
C. C.
D. D.