A 7.0-kg rock is subject to a variable force given by the equation
F(x) = 6.0 N - (2.0 N/m)x + (6.0 N/m2)x2
If the rock initially is at rest at the origin, find its speed when it has moved 9.0 m.
20 m/s
You might also like to view...
A rectangular flat water tank is placed on the roof of a house with its lower portion perfectly insulated. A sheet of glass whose transmission characteristics are tabulated below is placed 1 cm above the water surface. Assuming that the average incident solar radiation is 630 W/m2, calculate the equilibrium water temperature for a water depth of 12 cm if the heat transfer coefficient at the top of the glass is 8.5 W/(m2 K) and the surrounding air temperature of 20°C. Disregard intereflections.

GIVEN
- A glass covered water tank on the roof of a house
- Lower portion of tank is perfectly insulated
- Distance between glass cover and water surface
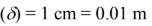
- Average incident solar radiation (Is) = 630 W/m2
- Water depth = 12 cm = 0.12 m
- Heat transfer coefficient on the top of the glass (hco) = 8.5 W/(m2 K)
- Surrounding air temperature (T?)
- Transmissivity of glass (??)
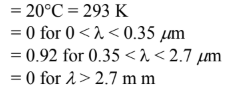
- Reflectivity of Glass (p?) = 0.08
FIND
- The equilibrium temperature of the water (Tw)
ASSUMPTIONS
- The effect of inter-reflections is negligible
- The water temperature is uniform (internal resistance of the water is negligible)
- Steady state conditions
- Is value given is normal to the glass surface
- The water absorbs all the radiation reaching it
- Water behaves as a blackbody
- The conductive thermal resistance of the glass is negligible
- The sky behaves as a blackbody enclosure at Tsky = 0 K
- The sun is blackbody at 6000 K (see Table 9.2)
- The shape factor between the surface and the glass can be taken to be unity
- The air properties are the same as dry air properties
- The glass acts as a black surface for the reradiated energy
SKETCH
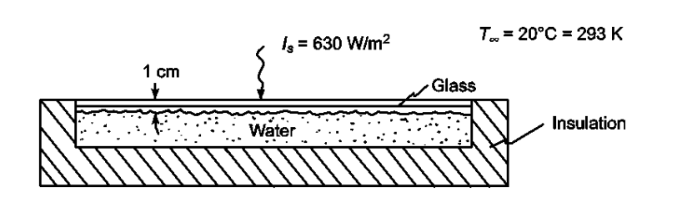
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?)= 5.67 x 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
The air resistance of falling is greatly affected by an object's frontal area and
A) mass. B) weight. C) speed.
What is "excluded" by the Pauli exclusion principle?
a. certain values of angular momentum b. precise values of both position and momentum c. electrons in the same quantum state d. none of the above
A ball is thrown straight up. At what point does the ball have the most energy?
(a) At the highest point of its path. (b) When it is first thrown. (c) Just before it hits the ground. (d) When the ball is halfway to the highest point of its path. (e) Everywhere; the energy of the ball is the same at all of these points.