Refer to the diagram where D and S are the United States' demand for and supply of Swiss francs. At the equilibrium exchange rate, E, the United States' balance of payments is in equilibrium. Under a system of flexible exchange rates, the shift in demand from D to D' will:
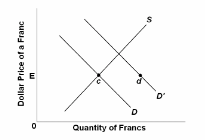
A. ultimately reduce U.S. exports and raise U.S. imports.
B. cause the dollar to appreciate.
C. cause the Swiss franc to depreciate.
D. cause the dollar to depreciate.
D. cause the dollar to depreciate.
You might also like to view...
The economy is experiencing a low rate of economic growth and the Fed decides to pursue an expansionary money policy. Which set of actions by the Fed would be most consistent with this policy?
a. Buying government securities and lowering the discount rate b. Selling government securities and raising the discount rate c. Buying government securities and raising the discount rate d. Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate
Scarcity:
A. exists because resources are unlimited while human wants are limited. B. means we are unable to have as many goods and services or as much time for activities as we would like to have. C. will likely be eliminated as technology continues to expand. D. is not an issue addressed in economics.
Which of the following does not explain the relatively low price inflation compared to the higher wage inflation in the U.S. during the 1990s?
A) the appreciation of the dollar B) a reduction in benefits paid to workers C) an increase in the natural rate of unemployment D) a reduction in the price of oil
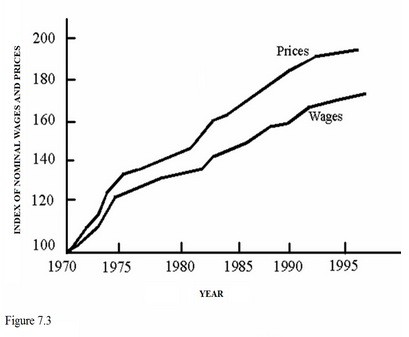 During the time period represented in Figure 7.3, the purchasing power of the average worker
During the time period represented in Figure 7.3, the purchasing power of the average worker
A. Decreased because nominal income decreased. B. Stay the same because COLAs reduced purchasing power. C. Decreased because real income decreased. D. Increased because nominal wages increased.